Escolhendo o certo laser source is one of the most critical decisions when buying a gravador a laser. Whether you’re customizing wood gifts, marking metal tools, or personalizing glassware, your engraver’s performance—and limits—are defined by the type of laser it uses. Neste artigo, we’ll break down the core types of laser sources (Co₂, fibra, e ultravioleta), explore their differences in wavelength and power, and help you decide which one suits your real-world needs.

What Is a Laser Source? (CO₂ vs Fiber vs UV)
A laser source in a gravador a laser is the component that emits the high-energy beam used to mark or cut materials. Different source types use different physics—and that greatly affects what materials they can engrave.
| Tipo | Comprimento de onda | Melhor para | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Co₂ | 10,600 nm | Organic materials like wood, couro, acrílico | Crafting, sinalização, embalagem |
| Fibra | 1064 nm | Metais, plásticos duros | Metal tags, ferramentas, peças industriais |
| ultravioleta | 355 nm | Heat-sensitive materials like plastic, vidro, cerâmica | Precision marking, eletrônicos, dispositivos médicos |
✅ Dica: The shorter the wavelength, the better it handles fine, heat-sensitive, or brittle materials.
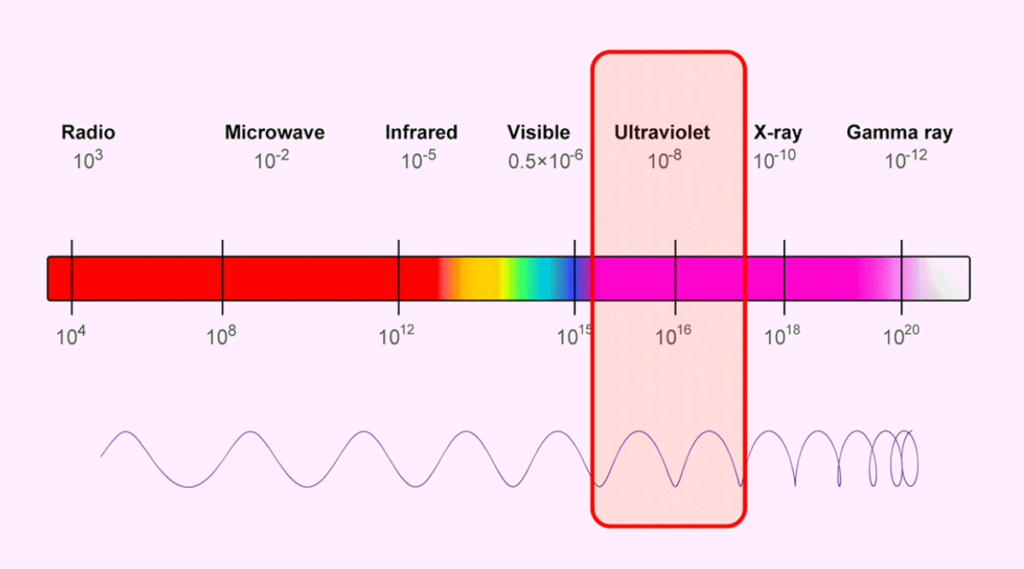
Why Wavelength Matters: Matching to Materials
O Comprimento de onda of the laser determines how deeply and cleanly it interacts with specific materials.
- Co₂ lasers (10,600 nm) are absorbed well by non-metals, making them ideal for engraving wood, acrílico, papel, e couro.
- Lasers de fibra (1064 nm) penetrate metals effectively due to higher photon energy at that wavelength.
- Laser UV (355 nm), like those used in the ComMarker Omni 1, are absorbed on the surface without heat buildup, making them perfect for plastics, vidro, e cerâmica.

Power vs Efficiency: Does Higher Wattage Mean Better Engraving?
Not always.
- Higher wattage means faster marking or deeper engraving—but only when paired with the right wavelength and lens system.
- A 5W UV laser can outperform a 20W fiber laser on plastic or glass, because the UV wavelength interacts better with those materials.
Here’s an example from real tests using the ComMarker Omni 1 Gravador a laser UV:
| Material | Fonte Laser | Power Used | Resultado |
|---|---|---|---|
| White ABS Plastic | ultravioleta (355nm) | 5C | High-contrast black mark, no melting |
| Aço inoxidável | ultravioleta (355nm) | 5C | Light surface mark only |
| Madeira | Co₂ (10,600nm) | 40C | Deep and wide engraving |
Choosing the Right Laser Source: What to Consider
When deciding which gravador a laser to buy, focus on:
- Material types you work with most
- Engraving depth vs. velocidade (Do you need surface marks or deep cuts?)
- Level of detail (Códigos QR, tiny text, fine lines? UV wins here)
- Orçamento (CO₂ lasers are usually more affordable for hobby use)

Real-World Use Case Examples
- A jewelry crafter working with gold and silver → Go for a laser de fibra
- A DIY creator customizing tumblers and wood signs → Best with a CO₂ laser
- A startup marking logos on phone cases, copos, and ceramic mugs → Choose a Laser UV, como o Omni 1
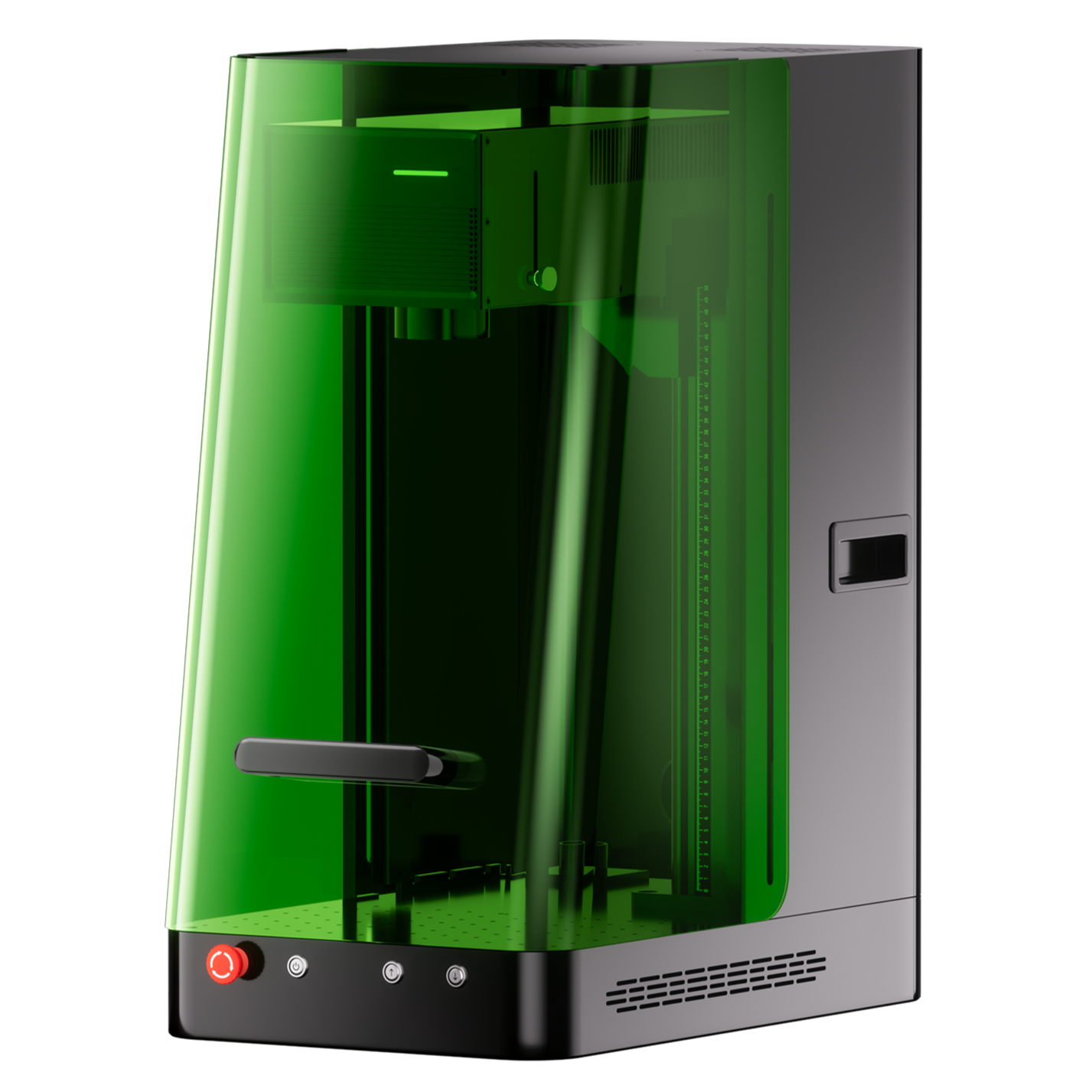
ComMarker Omni 1 gravador a laser
Laser de última geração para desbloquear todos os materiais. Tecnologia de gravação ZeroBurn™ O primeiro gravador a laser 16K HD do mundo Sistema de gravação SpeedMax™ de 10.000 mm/s Desbloqueie todo o material com laser UV Tecnologia térmica ColdFront™ Elevação elétrica com 2 Lentes opcionais compatíveis com sistema de gravação rotativa EZCAD e LightBurn 360°
Which Laser Source Is Right for You?
The best laser engraver isn’t just about power—it’s about matching the laser source to your application. If you’re engraving a variety of delicate or non-metal materials, o ComMarker Omni 1 Gravador a laser UV offers professional-level precision with minimal heat impact. For metals or bulk engraving, fiber and CO₂ still have the edge.
Need help choosing? Visita ComMarker. com to explore laser engravers tailored to your material needs.